What is entomophagy?
I get that question a lot (with the implied “why do you (and should I) care?”), and have worked to reduce my spiel down to an elevator pitch. My goal is to not just define the word, but tell why I care about entomophagy – give a convincing, but simple, explanation of why bugs are the best protein source for ethical and environmental reasons.
So I didn’t quite succeed at creating a quick pitch–there are too many important points to make! I’ll keep working on cutting it down into something that closer resembles an elevator pitch, but for now, here’s my… essay, really, with statistics help from Chapul, Exo, Crik Nutrition, Bitty Foods, Big Cricket Farms, the journal Science, Stanford, and the Coursera course from Johns Hopkins on the US Food system I took a couple years ago (see here, here, and here for relevant notes).
Most meat produced in the US is raised on factory farms, where animals are crammed together in cramped and dirty housing–a hardship for both animals and workers–and which pollute water, air, and soil, and drive down neighboring property values. *
Factory farmed animals are pumped full of antibiotics, chemicals, and hormones, and some farms feed industrial waste containing heavy metals to the animals. The sketchy things fed to food animals are later absorbed by human consumers. Remember, “you are what what you eat eats.” (Michael Pollan) Antibiotic misuse on factory farms breeds resistant strains of bacteria, which are transported off the farm via trucks, workers, meat, fertilizer, and even birds, and cause difficult-to-treat infections in humans. **

(credit: wongaboo; license)
Raising animals in industrial systems is extremely water- and land-intensive. ***
As the global need for protein continues to rise, the industrial farming system becomes less and less sustainable. Insects, specifically crickets, can be a nutritionally, ethically, and environmentally superior protein source to conventional meat.
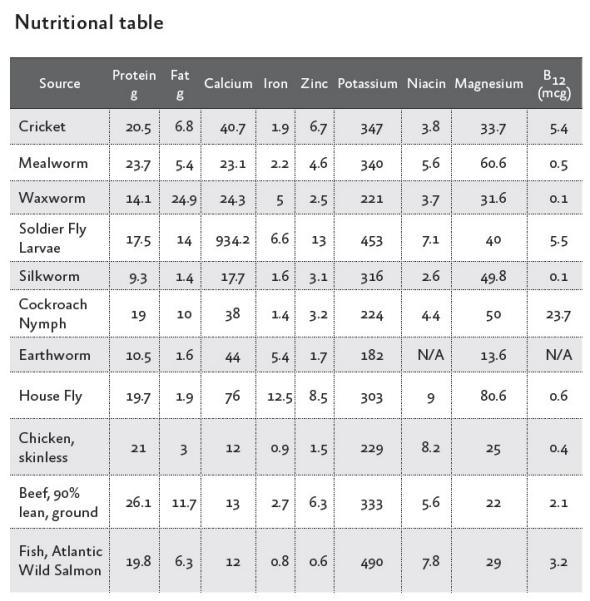
Crickets are an excellent source of protein and nutrients. They are lower in fat, and higher in iron and magnesium than beef, and are a complete protein source: they contain all nine amino acids essential to human and animal diets.
The environmental footprint of a cricket farm is minuscule compared to an industrial farm system. Pound for pound, crickets produce 1% as many greenhouse gases as cows and three times less waste. Crickets need 8% of the feed and water as cows to produce the same amount of protein, and are much more efficient as a protein source than cows: 100 lbs of feed produces 50-60 lbs of edible cricket protein, vs 5 lbs of edible beef. **** A cricket farm requires 2000x less land than a cow farm.
Crickets have a much shorter life span, and can be harvested at 6 weeks, which is much faster than cows at 18 months. North American farms raising crickets for human consumption feed organic diets without hormones, antibiotics, and pesticides (of course). Crickets are harvested humanely by dropping the ambient temperature to put them into a dormant hibernation-like state, and from there they’re deep-frozen. *****
People in poor countries need access to iron- and protein-rich meat sources, and a resilient system for growing it. Cricket farming could help solve that problem. According to the UN, if edible insects become a part of the mainstream global diet, we can reduce greenhouse gases by 18%, and lower the average cost of food globally by 33%. Other cultures all over the world eat bugs, and Americans are already eating bug parts at some levels in processed foods. Insect protein is the future, so you might as well start embracing it now!

(credit: shankar s; license)
For easy entry into the world of eating bugs, try cricket energy and meal replacement bars, cricket baked goods, and cricket protein powder from Exo, Chapul, Bitty Foods, and Crik Nutrition. For 10% off Exo bars, use code HAUTEPASTURE at checkout!
I had a lot of trouble limiting myself to a length that would make for a somewhat effective elevator pitch; hence, the asterisks above, for the following elaborations:
* Most people are aware of the terrible conditions for animals on factory farms, but the conditions can be horrible for workers too: exposure to chemicals, waste gases, particulates, hard labor, and illegals with no rights often must endure abusive hiring practices.
** Factory farms pollute water with waste storage failures and illegal dumping directly into waterways; air pollution comes from gases, particulates, and animal dander, and soil is polluted when waste is applied to land as fertilizer. For industrially produced meat products, the ratio of fossil fuel energy input to food energy produced out can be as high as 35:1, with beef produced in feedlots generally having the most unfavorable ratio.
*** 7% of global water is used to grow grain for livestock, and meat production uses 70% of farmland, 30% of Earth’s surface, and 40% grain grown globally. Meat production is an inefficient use of grain, water, and land: it takes 1000 kg water to produce 1 kg of grain. The grain required to produce 100 kg of beef, pork, and poultry is 700 kg, 650 kg, and 260 kg respectively. So, for beef, it takes 7000 kg of water to make 1 kg of beef.
**** Crickets require about one gallon of water per pound, about 2000x less than cows, 800x less than pigs, 500x less than chickens, 350x less than eggs, even 200x less than vegetables.
***** Usually then they’re boiled to clean them and remove wings and legs, and dried and pulverized into powder. Cricket powder alone is not very tasty, so it’s combined with other powders for cricket flour for baking, or protein powder for supplements.